Good day!
Good day!
Quite often, when working at a computer (laptop), one has to deal with an operation formatting disks, flash drives and other drives.
For example, to delete all data from them, in case of various failures and errors, to change the file system, etc. flash drives ...
I must note that it is far from always possible to format a flash drive without problems in the first possible way. That is why I decided to sketch out a note with several formatting options (I think it will be useful to everyone who cannot perform this operation, or who cannot decide on the file system in any way).
So...
👉 Supplement!
If, when formatting or when trying to copy files to a USB flash drive, you see an error that the drive is write-protected, I recommend that you familiarize yourself with this material.
Important!
Formatting will destroy all data on the drive. If the flash drive has the necessary files, copy them in advance to excellent media (make a backup).
*
Ways to format flash drives
About the choice of the file system and the size of the cluster
When formatting the drive (in any of the ways), you must specify file system, cluster size and volume name. And if you indicate the name of the difficulties does not cause difficulties, then with the rest, many have questions ... 👀
In general, the following file systems are most commonly used today:
- 👉 FAT32 - the oldest file system, which is supported by almost all devices (even various game consoles!). Most flash drives are formatted with this file system by default. It has one significant drawback: you cannot write files larger than 4 GB to it!
- 👉 NTFS - a more modern file system supported by Windows XP and higher (on Mac OS X it is read-only, on Linux there are distributions that support read-only, there are those that both write and read). File size - unlimited.
As for various consoles and devices, NTFS is not supported by all (for example, Xbox 360 or Sony Play Station do not support it). In general, NTFS is more suitable for disks (than for flash drives) that will be used in Windows.
- 👉 exFAT (or FAT64) is a specially designed file system for flash drives. Supports files larger than 4GB, disk partition size is not limited.
By the way, exFAT has one key advantage: it overwrites the same sector less during operation, which affects the lifespan of the drives (i.e. a flash drive with exFAT should work longer than with NTFS). That is why, for flash drives, it is preferable to use exFAT than NTFS.
*
👉 Conclusions
If you want maximum compatibility and plan to connect a USB flash drive to consoles or old PCs, choose FAT32 (however, you will be limited to a file size of 4 GB).
In other cases, it is preferable to choose exFAT (however, I note that some TVs, for example, cannot read this file system and it is for the sake of them that you have to choose NTFS).
*
What about the size of the cluster (or it is also called the unit of distribution)
This parameter is responsible for how much the flash drive will allocate space for one file. For example, if the standard cluster size is 64 KB, and your file weighs 50 KB, then it will take up 64 KB space on the flash drive!
If you are going to store a lot of small files on a USB flash drive, choose the minimum cluster size. However, in this case, the speed of the drive will be lower!
Most users, in my opinion, can ignore this setting, it is optimal to leave the value default .
*
Method number 1 - through "This computer" (explorer)
- We connect the USB flash drive to the USB port of the computer / laptop;

We connect the flash drive to the USB port
- We go into the explorer (the combination of buttons Win + E) and open "This computer" in the menu on the left. You should see your drive in the list of devices. If it is not there, go to the next formatting method.
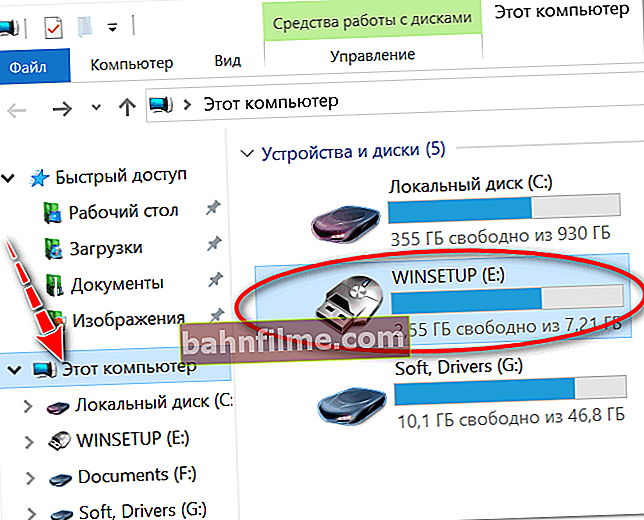
This computer - USB stick is connected
- Next, right-click on the flash drive and in the menu that appears, select "Format..." (see screenshot below 👇);
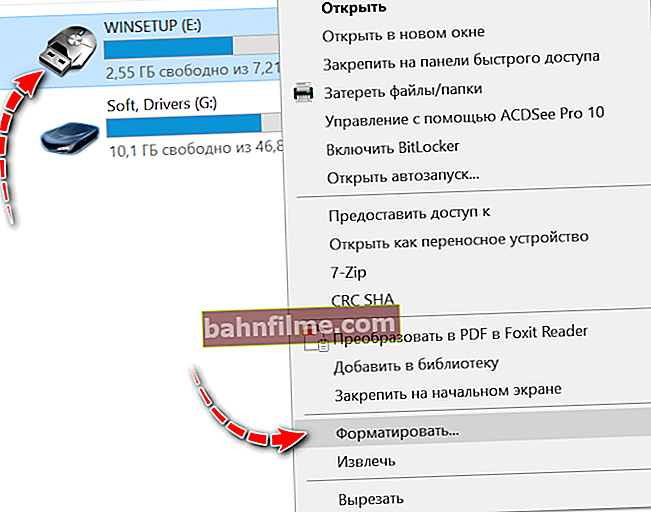
Format flash drive
- After that, a window will appear in which you need to select the file system and specify the distribution unit (cluster size). About what and in what cases to choose - I talked a little higher in the article. By the way, Windows will warn you that formatting will destroy all data on the media.
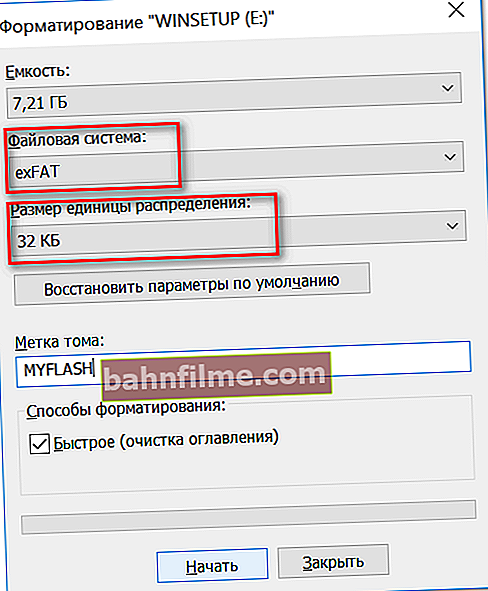
Choosing a file system and allocation unit
- Actually, after which you will get a clean USB flash drive to which you can transfer the necessary files ...
Blank flash drive ...
*
Method number 2 - through disk management
Not always and not all media are visible in "This Computer / My Computer". This may be due to a conflict of drive letters, if the flash drive is not formatted at all, in case of a file system failure, and in a number of other cases.
Naturally, if you do not see her in "On my computer" - then you won't be able to format it this way ...
However, Windows has a special tool - 👉 disk management ... It displays all drives connected to the system (even those with problems).
The universal way to open 👉 disk management :
- press the combination of buttons Win + R (the "Run" window should appear in the corner of the screen);
- then enter the command diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
*
You can also open Disk Management by going to 👉 Windows Control Panel and using search.
*
All disks, flash drives, and other media that your computer sees will be presented in the disk management. Just select the desired drive from the list, right-click on it and select from the menu "Format..." .

Disk Management - Format Drive
Next, a classic window will appear with the input of the volume label, cluster size and file system. Specify the required parameters and click OK. Actually, the task is completed ...

Volume label, file system, cluster size
*
Method number 3 - through the command line
In some cases, such as when the explorer freezes or an error appears "could not complete formatting" - you have to resort to working with the 👉 command line (note: it can also be used to format drives).
*
Important! Be careful, perform all actions step by step, as described below.
*
I'll show you everything with a personal example.
First you need to run 👉 command line as administrator.
To do this, open the Task Manager (shortcut Ctrl + Alt + Del or Ctrl + Shift + Esc), then press "File / new task" and enter the command CMDwithout forgetting to check the box "Create a task with administrator rights" (as in the example below 👇).

Running CMD with administrator rights
Next, a "black" command line window should open. I will write down all the commands in order (see the explanatory screen below 👇):
- first you need to find out the letter of the flash drive (if you haven't connected the flash drive to the USB port - plug it in!). To do this, enter the command diskpart and press Enter.
- then enter the list volume command and press Enter (note that in the list of drives you should see the letter of your flash drive! In my case, the letter "E", highlighted in yellow);
- then, to close diskpart, type exit and press Enter;
- to format, use the command format E: / FS: exFAT / Q / V: fleska (where "E" is the letter of your flash drive; FS: exFAT is the file system (for NTFS - enter FS: NTFS); V: fleska is the name of the flash drive, can be anything (for example, V: mydisk).

Working in the command line
Actually, after entering the last command, the formatting process should start. Only be careful and do not confuse the drive letter - many command line operations do not require confirmation! 👀
*
Method number 4 - using "low-level" formatting
There is one universal utility that can format a drive without paying attention to Explorer and errors in Windows (it works with the device directly *). This is aboutHDD LLF Low Level Format Tool (👉 link to the developer's site).
This utility is suitable for working with ordinary USB flash drives, as well as SD cards, external drives, etc.
The screenshot below (👇) shows how you can format the drive in it. For your flash drive - you will need to do the same.

Low-level formatting of a flash drive in HDD LLF Low Level Format Tool
An important point: after such a "low-level" formatting, you will need to do a high-level formatting (for example, as in method 1, 2).
*
Method number 5 - using special utilities (flash drive firmware)
If all other methods were unsuccessful, most likely something is wrong with your flash drive: a file system crash (for example, it may be marked as RAW); infection with viruses that block work with the drive, and so on.
In this case, you need to use special utilities (for the so-called flash drive flashing). Moreover, I want to note that in most cases, for each model of the flash drive, you will need its own utility (using a third-party one can damage it permanently)!
Below are some links to my articles, they will help you perform this operation!
👉 To help!
1) This article will tell you how to find a special utility and format even half-killed flash drives (which are not visible and freeze when accessing them).
2) A few more tips on what to do if the flash drive is not formatted are given in this article.
*
Additions on the topic - will come in handy!
That's all for now, all the best!
👋
First published: 03/14/2018
Correction: 09/29/2020