User question
Hello, Alexander.
Is there any way to compress video without losing quality? Not so long ago I downloaded a program (about which they wrote a similar thing) and tried it - the video still looked worse, the quality dropped noticeably ...
Hello!
In general, this is a fairly popular question, and often novice video-amateurs fall for this "bait" - you can compress any video, only there will almost always be a loss in quality!
Another thing is that in some cases - it is noticeable by eye, in others - even the experienced gaze of a moviegoer is not able to see the difference!
In this article, I want to talk in more detail about how to compress a video, and how, and in what cases, to do it "without losing quality" (note, the phrase is enclosed in quotes).
Educational program on video compression - reducing the size of a video file
A bit of theory: what you need to know for proper compression
Complex terms on video processing are deliberately removed from the article. The article is simplified as much as possible for its understanding by the most ordinary users who are faced with the problem of converting and compressing video.
In general, almost all videos (99.9%) that you find on the network (watch, download, etc.) are already compressed with some kind of codec. Uncompressed video - occupies a rather large size on disk (for example, one high-quality movie can take several terabytes!).
So, the key here is that different codecs work according to different algorithms and provide different file compression rates. Naturally, this also affects how your file will be displayed later, after compression, and how much disk space the file will take.
Thus, in order to be able to compress a video without losing quality, you need to proceed from 2 points:
- if the video was compressed with a "weak" codec (which provides far from the maximum compression), then you can compress it and reduce the size of the video file without degrading the picture quality (by the way, as a rule, in this case, you need a more powerful PC for viewing. For example, MPEG2 video can be watched on a weaker PC (without jerks and delays) than, say, MP4, well, I'll say a few more words about that below);
- from the device on which you want to watch the video. For example, if you watch a video on a small screen with a low resolution, then the difference in the quality of the video (be it 1 GB or, say, 300 MB) - you simply will not notice! To see the difference, you need to open the video on some big TV screen.
That is, I think my message is clear: if you watch video on a screen with a resolution of 1024x768 (or in such a "window" in Windows, and work in the next one ...), and your video quality is 1920x1080, this video can be compressed. to a lower resolution and better codec.
By the way, here we must not forget about one more parameter - bitrate (for the number of bits used to store one second of multimedia content, see Wikipedia).
The higher the video resolution, the higher the bitrate should be. If the bitrate is very high, then it can be reduced to reasonable limits when compressing the file.
For example, the maximum bitrate for creating a Blu-ray disc is 35 mbps. So, the difference between 30 and 35 is not easy to notice, but between 5 and 35 is striking ...
Note: It is now popular to download videos to your phone / tablet and then watch them somewhere on the road. So, such a video is not only possible, but even recommended to be compressed, and then downloaded to your mobile device.
Here's the thing: firstly, the compressed video will take up less space on your flash drive (and mobile devices do not have that much memory); and secondly, the video will not slow down (as is often the case with an unprepared video for downloading to mobile devices).
*
On codecs and containers: what to try and what not to compress
There are dozens (if not hundreds) of video formats in which it is distributed.Each format has its own disadvantages and advantages, some of them are already outdated, others, on the contrary, have just appeared.
In this small subsection, I want to focus on the most popular formats that I have to deal with, and also say a few words about the advisability of compressing one format or another.
Note: By the way, you should distinguish between codec and container. For example, the file format is AVI (this is the container), and it can be compressed using various codecs: Microsoft VC-1 or x.264 (for example).
About Codecs
👉 Large selection of codecs for Windows - presented in my selection ->
x.264 / MPEG-4 AVC is probably the most widely used codec. It is used in most video and photo cameras in which the captured frames are stored on hard drives, memory cards, etc. x.264 is probably becoming the most popular codec. Adobe supports it in Flash movies, x.264 can be used with images in HTML 5.
MJPEG (Motion JPEG). An old video compression codec. It is outdated today, we use it little.
MPEG-2. There is the MPEG-2 codec (known as x.262) and there is also the MPEG-2 container format. MPEG-2 is used for DVD video and over-the-air TV signals. In general, it provides an optimal quality / file size ratio. Supported by almost all players.
Microsoft VC-1. Microsoft VC-1 is used as an alternative to Adobe Flash technology and is used in the Microsoft Silverlight Internet platform. Provides medium quality compression.
MPEG-1. Obsolete video compression codec (replaced by MPEG2). Previously, such a video could be found on CD-ROMs. Now it is less and less common, although if you like to watch old videos - you probably meet with him.
WMV. There is a Windows Media Video codec, and there is a container of the same name. Provides a very high quality video compression, with a fairly good picture. Very popular and widespread.
DivX is a video codec, various versions of which comply with the MPEG-4 part 2, MPEG-4 part 10 (MPEG-4 AVC, H.264) standards.
Xvid (formerly "XviD") is an MPEG-4 Part 2 video compression library. By the way, the compression methods used in MPEG-4 are patented, so it may be illegal to use Xvid in some countries.
About containers
There are dozens of containers now, each with its own pros and cons. The container, in addition to compressed video with any codec, also contains sound (which is also compressed. Audio, as a rule, takes up quite a bit of space, so I don't consider audio codecs, their effect on the file size is not significant).
AVI (or Audio Video Interleave) is one of the most popular containers from Microsoft. Most often, video on a PC is found in this format. By the way, many for some reason do not recommend compressing modern video into this format.
MP4. This container format was developed by Motion Pictures Expert Group. Many users call it MPEG-4. Usually, video in MP4 files is encoded with the x.264 codec, and the audio is encoded with the AAC codec. Sometimes, there may be other codecs in this container ...
VOB and BDAV MPEG-2. Used for packaging videos on DVD and Blu-ray discs. Blu-ray discs (.m2ts) can contain videos compressed with the x.264 and VC-1 codecs.
ASF (Advanced Systems Format) - Found in several extensions .asf, .wma, and .wmv. By the way, it is most likely that the .wmv file is compressed with the WMV (Windows Media Video) codec, but the file itself is placed in an ASF container file.
QuickTime. The brainchild of Apple. The container supports many audio and video codecs. Apple is a supporter of x.264, therefore, QuickTime files (formats: .mov, .qt) most often contain video compressed with the x.264 codec.
Flash. Adobe's Flash container format is quite popular, by the way.
Matroska (.mkv, .mk3d, .mka, .mks) is a very popular and demanded container today. Free, open - this is probably why it became widespread. Many high quality videos are distributed in this container.
DiVX. Both codecs and container are very common. The format is also of the same name - ".divx". By the way, the codec has a "pirate" origin, which allows you to get high quality video with strong compression.
For a while, Divx was not recognized by "big" equipment manufacturers, however, today many already embed DiVX hardware codecs into most equipment (if it were not for the popularity of video files of this format, nothing would probably have happened ...).
Which codec and container to choose
- If you want to get the maximum video compression, it is logical to choose the x.264 codec, which provides excellent compression with good quality.However, keep in mind that not all hardware (especially not the newest) allows you to view such files. If the video in very high resolution - even modern low-power PCs will not be able to play it and show it without delays and freezes. By the way, if the video is not compressed by any variation of the x.264 codec (for example, it is in MPEG1, 2 or some other format) - it can be compressed without loss of quality into a more "compact" codec (say, Divx) .
- If you plan to watch the files on DVD-players, various devices, etc. - it is recommended to choose the codec and the MPEG2 container - it is supported by almost all equipment;
- For various films, clips, cuts from the finished video - the MP4 container is excellent, as a good compromise between the compression ratio and quality.
*
Compress video step by step: 2 ways
The first way
Video Master 👍
Website: //video-converter.ru/ (note: included in the "Video Studio" package)

An excellent program for compressing and converting various videos: both movies that you want to fit on a disk or flash drive, and home videos that you need to compress. Supports all the most popular formats and codecs that are only found: AVI, MP4, MPEG, MKV, DIVX, MP3, etc.
What's even more pleasing: the video can be improved when converting: change the brightness, remove noise, crop the edges, and cut out unnecessary fragments from it.
By the way, what else I want to note: the program allows you to specify in advance what file size you need (which is very convenient). Completely in Russian, compatible with Windows 7, 8, 10.
👉 To help!

Video enhancement: examples and effects for a beginner!
Here's an example of how to convert a movie or movie:
- First, download and install the program (the link is given above). Then run it and add the file you want to compress (screen below, "Add" button 👇);
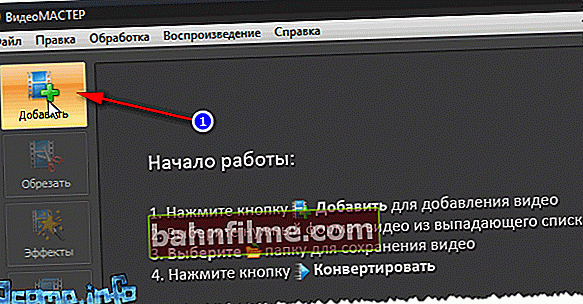
to add a file
- Next, I recommend immediately pressing the button "Trim" and cut out everything you don't need. In principle, there is nothing complicated about the operation itself: just find a section in the video that you do not need, then mark it with sliders and cut it out. There can be many such fragments (example on the screen).
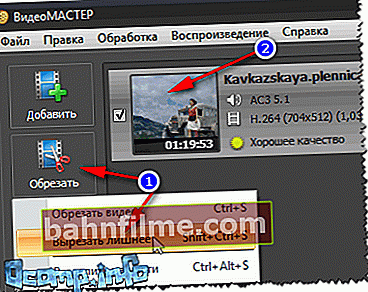
Cut out the excess from it
- Then press the next button - effects.

Effects
A window will open in which you can decrease / add brightness, saturation, etc. Tabs will also be available to you:
- cropping (to change the size of the video resolution, position of the picture, and change the aspect ratio);
- text (you can add test fields to the video);
- improvements (for example, auto-contrast, noise reduction, defect elimination);
- turn (it will help if you need to rotate the video 90 degrees, it often happens when shooting video on your phone);
- speed (you can increase / decrease the playback speed of the file).
In general, set the settings for yourself!

Editing video
- Then you need to specify container and format (which was discussed a lot at the beginning of the article). To do this, click on the button Format / AVI (by default, this is the format selected). Video Master offers to save video in a wide variety of containers and codecs: AVI, MPEG4, MTS, WMV, ASF, MPEG 1, 2, etc. I chose the MP4 format for my video.
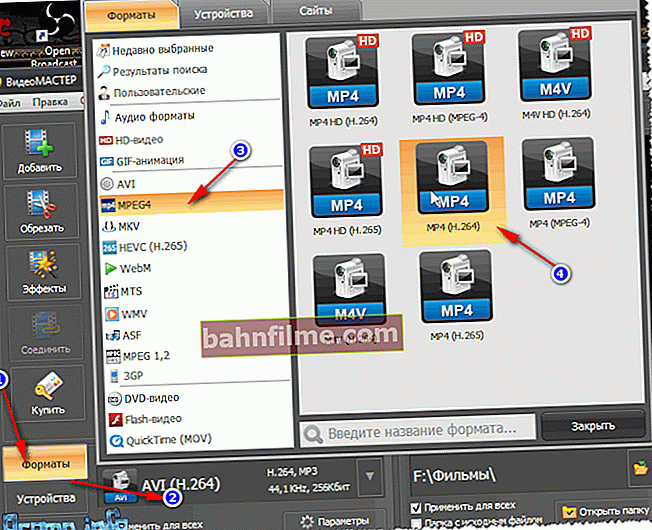
Choosing a container and codec
- Next specify video resolution and quality (bitrate). In general, in this regard, the program is excellent: it allows you to manually set the size of the resulting file: this way you can immediately determine whether it is good or bad quality, it will work. In general, for example, I decided to fit the video to the size of the CD-disk, so manually indicated a size of 701 MB.
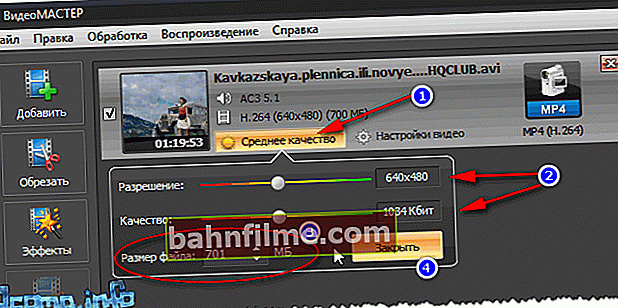
Choice of size and resolution
- Next step: specify where the resulting file will be saved , and start, in fact, conversion ... There is nothing complicated here, it is shown in the screenshot below (the "Convert" button).

Choosing a place to save and launching the envelope
- The conversion process is quite lengthy and depends on many parameters: on the power of the PC, on the codec and container you have chosen, on the source video, etc. In general, this task was completed!

Conversion process
*
Second way
Movie Shrink & Burn (Ashampoo)
Website: //www.ashampoo.com/

I cannot but mention this program from Ashampoo - an excellent and fast converter of various video files (supports more than several hundred formats). What else is captivating: there is nothing superfluous in the program, the program is very easy to use, everything is done in steps (however, this is almost in all programs from this manufacturer).
Movie Shrink & Burn allows you to burn DVD / Blu-ray discs, burn videos for various devices, upload files to the cloud.
Supported mobile devices: Apple, Sony, Android, Microsoft, videos can be saved in a variety of quality: 720p, SD (high, low).

For which devices you can prepare video
The program fully supports the Russian language, compatible with all versions of Windows.
Perhaps, it is inferior to the first in only one thing: there is no possibility to crop a video, cut out something unnecessary from it, glue something, rotate it (i.e., there is no mini-editor).
I will consider an example of converting a regular video file step by step:
- The first thing we do is run "converter" .
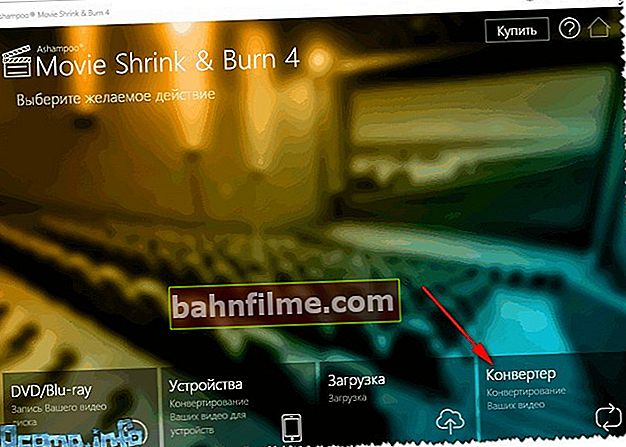
Launching the converter
- Then add some file (or even a folder with files).
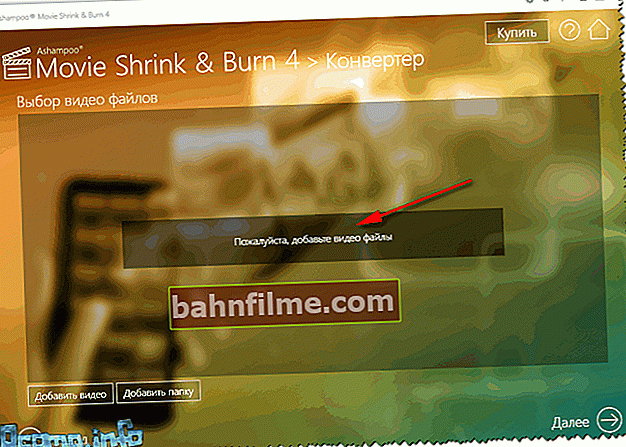
Adding a file
- Then we indicate the container and codec. By the way, there are not many containers in the program - but all the popular ones are represented: AVI, WMV, MPG, MP4, MKV (I think that the ones presented are above the roof 👌).
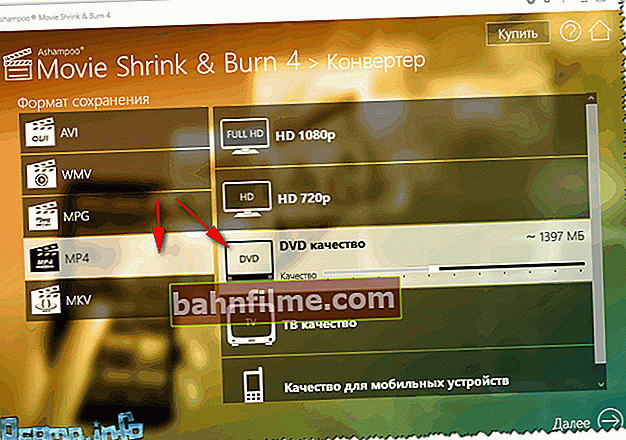
Choice of format and codec
- Next, specify the folder (disk) where the resulting video will be saved after conversion.

Where to save the file
- The final touch - the conversion process will start, you just have to wait until the process is completed.
File conversion process
*
That's all for me, all high-quality and compact videos.
Add-ons are welcome!
Good luck!
👋
First publication: 16.02.2017
Correction: 01/05/2020